The digital era brought about an incredible wave of connectivity and accessibility. It lets businesses tap into the power of data in ways we couldn't even dream of before. But with all this data flowing in, there's always the risk of getting swamped by chaotic, scattered, and sometimes unreliable information. Unless companies follow proven data management best practices, they're in for a real struggle trying to make sense of the data and find the gold nuggets to stay in the game.
When 76% of business leaders find it difficult to understand their data, know that collecting it is just not enough. Why? Simply because it is not managed strategically. We may say it is merely energy wasted unless businesses keep up with the latest practices in data management. This is exactly what our article aims to cover today.
Let’s dive into 10 data management best practices and the tools you need to help you soar way above the competition.
10 Data Management Best Practices That Deliver Results
Having a well-structured data management system is the key to getting the most out of your data assets while keeping sensitive information safe. This means setting up strong data management processes and implementing optimal processes that cover all the integral parts of your strategy. So, without further ado, here are the 10 best practices for data management that are practically a guarantee for unmatched results.
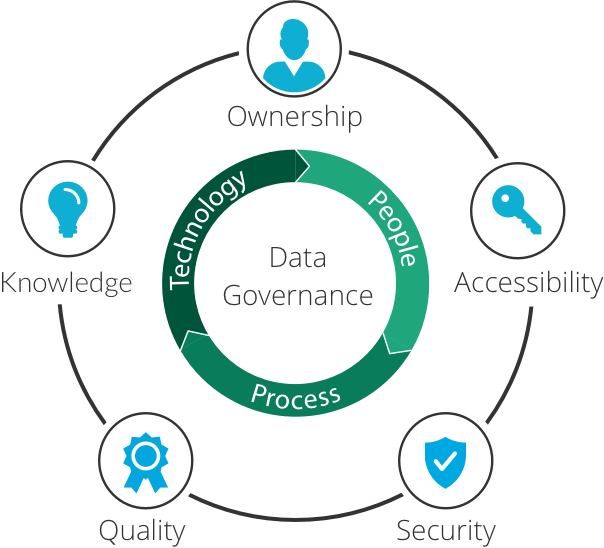
Best Practice 1: Implement Data Governance
Data governance forms the foundation of effective data management. It is a strategic approach that outlines the rules, processes, and responsibilities for managing an organization's data assets. The data governance program guarantees that data is accurate, consistent, secure, and used appropriately across the organization. Here are a few concepts to keep in mind to ensure you establish good data management practices:
- Develop Governance Structure & Roles: Establish a clear organizational structure for data governance. Define roles like data owners, stewards, and a governance committee to clarify responsibilities.
- Implement Policies & Procedures: Develop comprehensive data governance policies to provide guidelines for data handling and ensure consistency across the organization.
- Define Data Ownership & Accountability: Assign data stewards or owners for different datasets to ensure that someone is responsible for the quality and accuracy of the data.
- Data Flow Visualization: Document the end-to-end journey of data as it moves through various systems, processes, and transformations. Visualizing data lineage helps to understand how data is created, modified, and used across different stages.
- Impact Analysis: Use data lineage to assess the potential impact of changes or updates to data sources, systems, or processes.
- Data Compliance & Regulations: To avoid legal and financial consequences, make sure that data management practices adhere to industry-specific regulations and data protection laws (like GDPR, HIPAA, etc.).
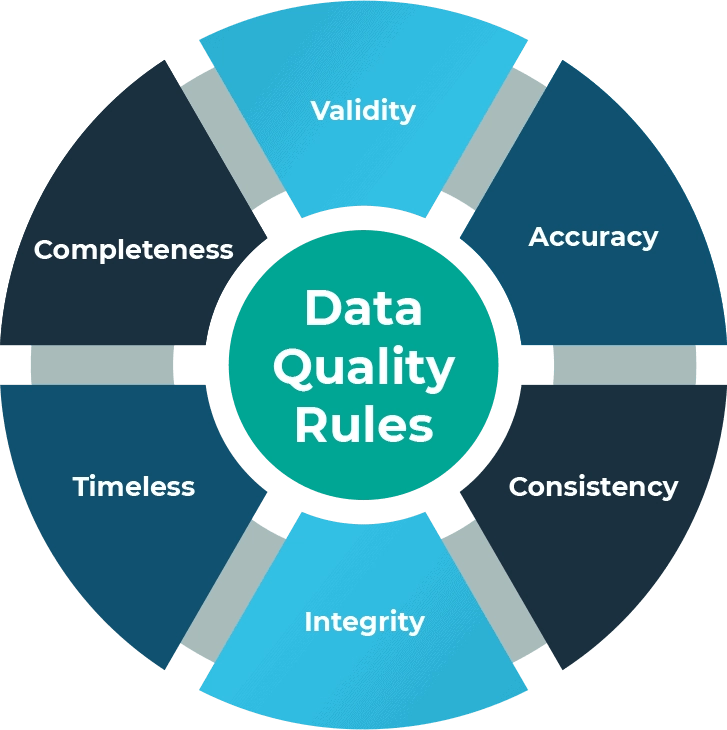
Best Practice 2: Data Quality Management
Data quality management focuses on maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data. Poor data quality causes incorrect decisions, operational inefficiencies, and eroded customer trust. Let’s look at how you can maintain high-quality data.
- Data Standardization: Enforce consistent formats, units, and definitions across datasets to improve data consistency and usability.
- Data Profiling & Cleansing: Analyze data to identify inconsistencies, errors, and duplicates, and then clean or rectify them so that the data is accurate and reliable.
- Data Validation: Implement validation checks during data entry, integration, and transformation processes to prevent the introduction of incorrect data into the system.
- Data Monitoring & Maintenance: Continuously monitor data quality metrics and perform regular maintenance activities to keep data accurate and up-to-date.
- Data Quality Profiling Tools: Use data profiling tools to automatically analyze datasets for issues like missing values, inconsistencies, and duplicates.
- Root Cause Analysis: When data quality issues arise, perform root cause analysis to determine the underlying reasons. This will help address the core issues rather than just treating the symptoms.
- Data Quality Reporting: Create regular reports that provide insights into data quality metrics, trends, and improvements.
Best Practice 3: Prioritize Data Security & Privacy
In today's time, when there are more instances of data leaks and worries about personal information, it's really important for any company that deals with customer data to keep that information safe. Here’s how you can achieve it.
- Encryption: Encrypt customer data both at rest and in transit.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a data breach.
- Regular Data Security Audits: Conduct routine security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your data management processes.
- Data Classification & Segmentation: Classify data based on its sensitivity and criticality. This way, you can optimize resource allocation for sensitive data.
- Privacy by Design: Implement a "privacy by design" approach when developing new data management processes or systems. Ensure that privacy and security are integral from the start.
- Anonymization & Pseudonymization: Whenever possible, anonymize or pseudonymize customer data. This reduces the impact of a potential breach since the data would be difficult to associate with specific individuals.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls so that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive customer data. Role-based access ensures that employees can only access the data relevant to their responsibilities.
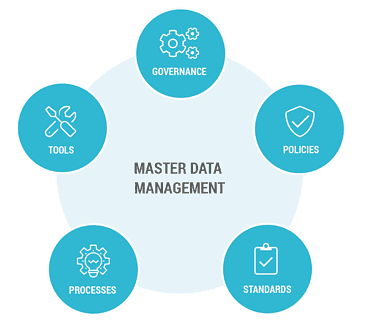
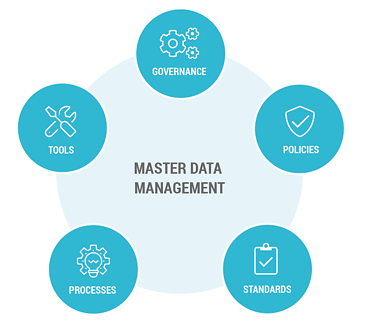
Best Practice 4: Master Data Management (MDM)
Master Data Management, also known as MDM, is a set of practices and technologies to create and maintain a consistent, accurate, and authoritative source of critical business data. The primary goal of MDM is to establish a single source of truth for data entities like customers, products, suppliers, employees, and more.
This single source of truth ensures that all departments and systems within an organization are working with consistent and reliable data. Let’s see how you can achieve this.
- Define Important Entities: Start by identifying the pivotal data entities that are the foundation of your organization. Think of customers, products, locations, and other critical elements that MDM will govern.
- Data Governance Collaboration: Intertwine MDM with strong data governance. Establish clear ownership and guidelines for maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and security of your master data.
- Standardized Data Model: Develop a standardized data model that defines the structure and relationships of master data entities across the organization.
- Central Repository Establishment: Create a master repository where accurate and standardized data resides and streamlines access and updates.
- Integration for Synergy: Integrate your MDM system with other operational tools and platforms to ensure data consistency across the organization.
- Relationship Mapping: Map out the relationships between different data elements. Understanding how data interrelates will improve contextual understanding and data accuracy.
- Change Management Strategy: Introduce MDM as a transformational initiative. Develop a comprehensive change management plan to guide employees through the transition.
- Continuous Monitoring & Improvement: Continuously monitor and improve data quality, gather feedback, and refine your MDM strategy to align with evolving business needs.
- Data Migration Strategy: If transitioning from existing systems, develop a strong data migration strategy for smooth and accurate data transfer to the new system.
Best Practice 5: Develop a Backup & Disaster Recovery Strategy
Having a solid backup and disaster recovery (DR) strategy ensures that no matter what unforeseen circumstances arise, your data remains intact and accessible. Here are some strategies that you can implement.
- Identify Critical Data: Identify what data is critical for your business operations. This includes customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and any data that, if lost, could severely impact your organization.
- Backup Frequency: Determine how frequently backups should be performed. For mission-critical data, consider frequent backups while less crucial data will require less frequent backups.
- Data Classification: Classify your data based on its importance and sensitivity. This will help allocate appropriate resources based on the data criticality.
- Backup Types: Implement a combination of full, incremental, and differential backups. Full backups capture the entire dataset, while incremental and differential backups capture only the changes.
- Off-Site Storage: Store backup copies off-site or in a remote data center.
- Automated Backup Solutions: Implement automated backup solutions for regular and consistent backups. It minimizes the risk of human error and ensures backups occur as scheduled.
- Test Restoration: Regularly test the restoration process for your backups.
- Documented Recovery Procedures: Create well-documented recovery procedures that outline the steps to follow in case of data loss.
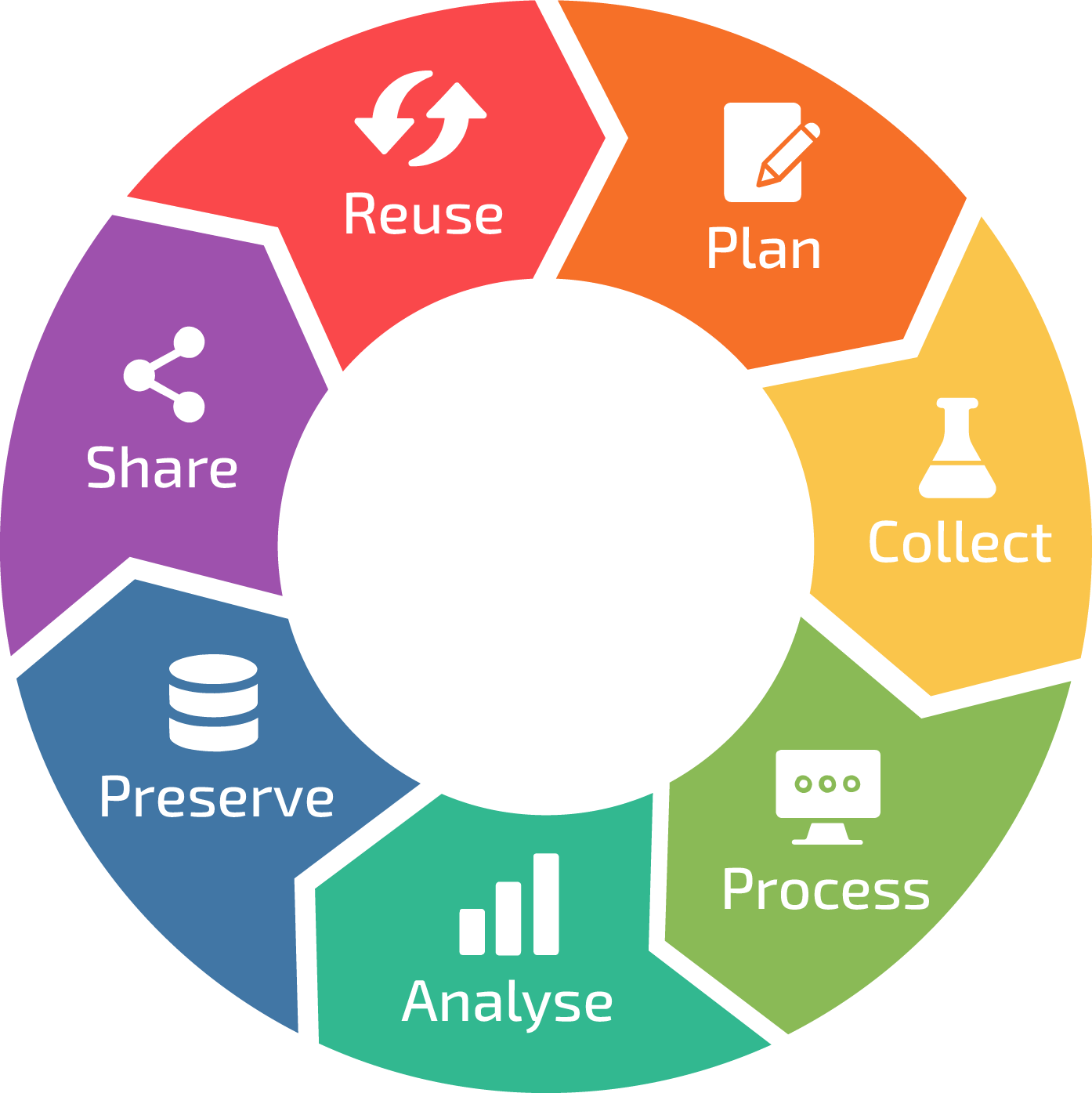
Best Practice 6: Data Lifecycle Management
This practice is about handling data from its birth to retirement to ensure its relevance, security, and compliance throughout its journey. Data lifecycle management gives you a roadmap that guides your data from creation to eventual archiving or disposal. Let’s take a look at some strategic best practices.
- Data Creation & Collection: Implement data creation guidelines that provide consistency and accuracy right from the start. Collect only the data that aligns with your business needs to avoid unnecessary clutter.
- Data Storage: Determine the appropriate storage solutions for different types of data.
- Data Inventory: Catalog your data assets. Understand what data you have, where it's stored, who owns it, and its importance to your organization's operations.
- Data Archiving: As data ages and becomes less frequently used, archive it in secure, long-term storage. This clears up active storage space while keeping the data accessible if needed.
- Data Retention Policies: Develop clear policies that outline how long specific types of data should be retained.
- Regular Data Review: Periodically review your data inventory. Remove outdated, redundant, or irrelevant data to maintain a streamlined and efficient dataset.
- Data Transformation & Migration: When systems or technologies evolve, ensure that data can be transformed or migrated easily to new platforms without loss of integrity.
- Data Disposal: Define secure methods for disposing of data that has reached the end of its lifecycle. This can include physical destruction or digital wiping, depending on data sensitivity.
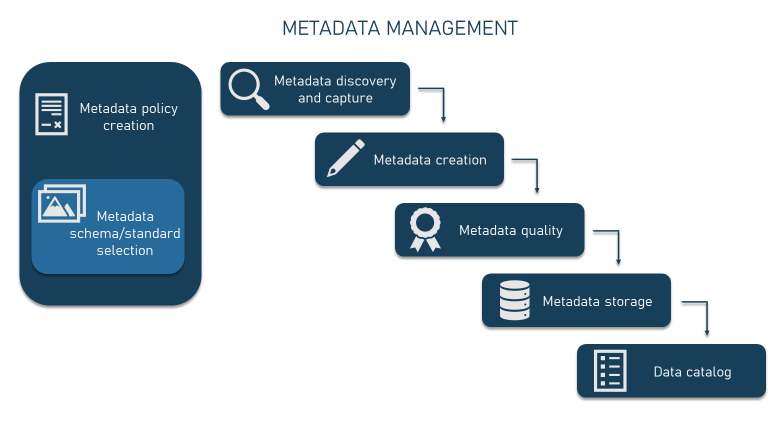
Best Practice 7: Ensure Metadata Management
Metadata – data about data. It's the information that describes your data, like its source, creation date, format, and relationships. Metadata management is a practice that might not make headlines but is necessary for maintaining data accuracy, understanding, and discoverability. Here are the proven strategies you implement.
- Catalog Your Metadata: Just like a library's catalog, create a comprehensive catalog of your metadata. Document its types, sources, and attributes to establish a clear reference point.
- Standardized Metadata: Implement standardized metadata formats and definitions across your organization to improve data understanding and interoperability.
- Data Relationships: Capture and maintain metadata that highlights relationships between different datasets.
- Metadata Tools: Invest in metadata management tools that help automate metadata collection, organization, and maintenance.
- Business Context Integration: Connect metadata to the business context. Understand how data is used in various business processes to ensure relevant metadata attributes are captured.
- Change Management for Metadata: Implement change management practices for metadata updates. Any changes to data structures should be reflected in corresponding metadata documentation.
- Metadata Audits: Regularly conduct metadata audits to ensure accuracy and relevance. This ongoing process maintains the quality of your metadata repository.
Best Practice 8: Invest In Data Storage Solutions
When you implement a data storage solution, it gives you a safety net to ensure that as data keeps pouring in, your storage infrastructure won't crumble under the weight. Here’s how you can pick the best data storage solution.
- Assess Current Needs: Start by understanding your organization's current data storage requirements. Analyze data growth rates, types, and performance demands to gauge your immediate needs.
- Plan for Future Growth: Predict your future data storage needs and ensure your chosen solution can accommodate this growth.
- Cloud Storage Options: Explore cloud storage solutions that offer scalability on demand. Cloud platforms let you scale up or down based on your data requirements.
- On-Premises Scalability: If on-premises storage is your choice, opt for scalable storage solutions that let you add more drives or expand existing systems without causing disruptions.
- Data Redundancy: Look for storage solutions that provide redundancy options like RAID configurations or replication.
- Vendor Support & Reliability: Research vendors thoroughly to ensure they offer reliable support and maintenance services.
- Data Tiering: Implement data tiering to allocate different types of data to appropriate storage tiers based on their usage patterns.
- Integration Capabilities: Choose storage solutions that integrate with your existing data management ecosystem, including backup, analytics, and other processes.
- Cost Efficiency: Consider both short-term and long-term costs. Scalable solutions should offer cost benefits as you expand and they should be financially sustainable over time.
- Data Security: Prioritize data security when selecting storage solutions. Invest in solutions that offer encryption, access controls, and advanced security features to protect your data.
Best Practice 9: Promote a Collaborative Data Environment
Perhaps it is the most underrated practice. A collaborative data environment cultivates a culture where data isn't locked away but is accessible and utilized across teams for innovation and better decision-making. Let’s discuss the specifics.
- Unified Analytics Platform: Implement an analytics platform that different teams can access.
- Collaborative Tools: Use collaboration tools that let teams annotate, comment on, and share insights about specific data points.
- Regular Data Sharing Sessions: Organize regular sessions where teams can share their findings, insights, and challenges related to data.
- Data Literacy Training: Provide data literacy training to employees across departments. When everyone speaks the language of data, collaboration becomes smoother.
- Transparent Communication: Encourage open communication about data projects. Transparency eliminates misunderstandings and helps teams align their efforts.
- Leadership Support: Gain leadership buy-in for your collaborative data environment. When leaders champion collaboration, it becomes a part of the organizational culture.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Create cross-functional teams comprising members from different departments. Diverse perspectives ensure that data is analyzed holistically for better insights.
- Joint Projects: Initiate joint data projects that require input from multiple teams. Collaboration fosters a sense of ownership and encourages a shared approach to problem-solving.
Best Practice 10: Introduce a Data Management Software
Introducing data management software is a critical step if you are looking to efficiently handle, store, and utilize your data. Whether dealing with customer information, sales records, operational data, or any other form of data, having quality data management software can greatly improve productivity and accuracy. Here are a few things to consider when introducing data management software.
- Research Thoroughly: Do in-depth research to identify data management software solutions that align with your organization's size, industry, and goals.
- Automated Workflows: Choose software that offers automation for routine data management tasks.
- Reporting & Analytics: Opt for software that provides advanced reporting and analytics capabilities.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor's reputation, reviews, and track record in the data management industry.
- Customization Options: Look for software that can be customized to match your specific data management processes.
- Data Enrichment: Look for software that supports data enrichment to enhance your datasets with additional contextual information.
- User-Friendly Interface: Prioritize software with an intuitive interface. User-friendliness minimizes the learning curve and encourages widespread adoption.
- Version Control: Consider software that incorporates version control features for data assets. This prevents confusion and ensures that the most up-to-date data is used.
How Estuary Flow Can Help Improve Your Organization’s Data Management
Estuary Flow is our advanced DataOps platform that can help with data management in several ways. It introduces an innovative way to handle real-time data processing efficiently and comes with a strong set of tools to manage various data needs. Whether you're replicating data or migrating it, Estuary Flow ensures your data is there when you need it the most.
Here’s how Flow can improve your data management
- Improving Data Quality: Estuary Flow helps clean and enrich data which can improve the quality of data for analytics and decision-making.
- Reducing Data Silos: Flow integrates data from disparate sources which can help break down data silos and improve data accessibility.
- Data Transformation: It transforms data as it is captured or loaded into a target system. This can be used to clean, enrich, or aggregate data to make it more useful for downstream applications.
- Scalability: It is designed to be scalable. It can handle large volumes of data and concurrent data flows. This makes it a good choice for organizations that need to manage a lot of data.
- Data Governance: Flow can help you enforce data quality and compliance standards. This can be done through tracking data lineage, auditing data access, and managing data retention policies.
- Real-time Data Integration: It continuously captures data from a variety of sources, including databases, SaaS applications, and streaming data sources. This gives you access to real-time data for analytics and decision-making.
- Data Collaboration: Estuary Flow is also designed to be collaborative. Multiple users can work on the same data flows at the same time and changes are automatically propagated to all users. This makes it easy to get everyone on the same page when it comes to data management.
The Takeaway
It's pretty much a consensus that the repercussions of neglecting data management can be severe – from missed growth opportunities and compromised customer experiences to regulatory non-compliance and security breaches. There's a solution to all these challenges and it's all about following data management best practices.
Estuary Flow will revolutionize the way you manage your data. Its innovative no-code features not only streamline the process of building data pipelines but also handles varying data requirements. Flow optimizes data movement for speed, scalability, and reliability and lets you take advantage of real-time analytics and data management software.
Are you ready for a streamlined data future? Sign up for free today or get in touch with us for more details.

About the author
With over 15 years in data engineering, a seasoned expert in driving growth for early-stage data companies, focusing on strategies that attract customers and users. Extensive writing provides insights to help companies scale efficiently and effectively in an evolving data landscape.
Popular Articles