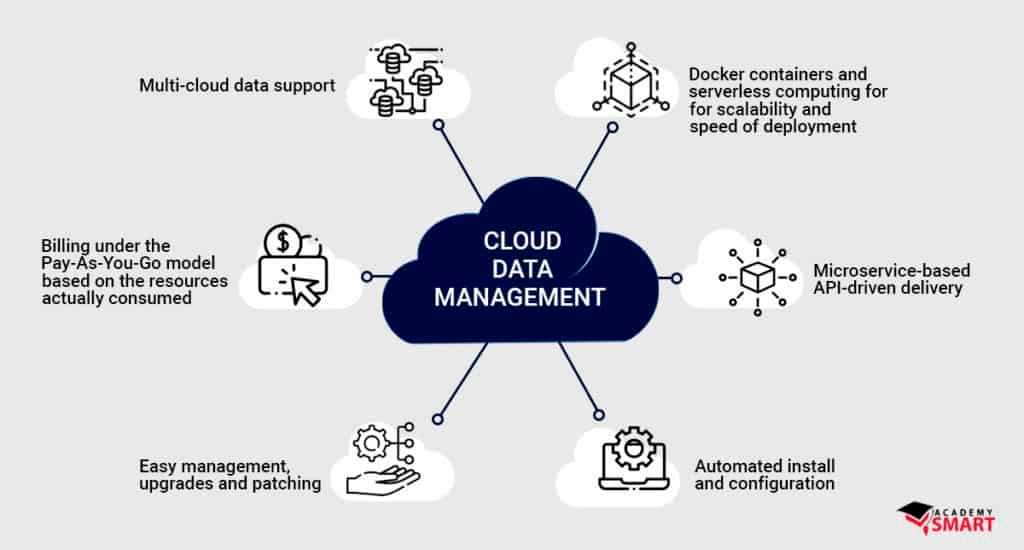
Managing data these days is not as easy as it used to be. From keeping it secure to making it easily accessible, companies face a lot of challenges. Cloud data management can help solve these problems. It gives you a secure and flexible way to store, organize, analyze, and share data.
When we say data, we're talking about a massive amount of it. Just to give you an idea, we expect to see 100 zettabytes of data stored in the cloud by 2025. That shows how important cloud data management will be in the coming years.
But, before you get too excited, you should know what you’re getting into. Cloud data management comes with its risks. A lack of effective strategies in cloud data management can make it tough to get the most out of your data. The only way out is to have a solid understanding of how to manage data in the cloud and what it entails.
That’s exactly what we’ll explore in this guide. We’ll discuss the importance and benefits of cloud data management and also talk about the risks if you don't have the right cloud data management practices in place.
What Is Cloud Data Management?
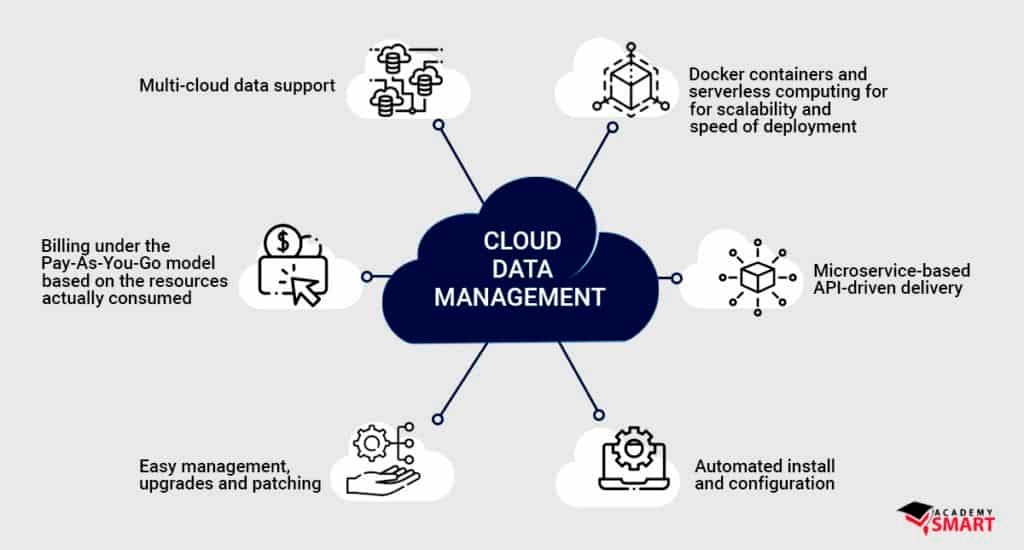
Cloud data management is the practice of controlling your company’s data using special tools, policies, and rules designed for the cloud computing environment. It is a system that helps you keep track of your files, databases, and other information when they are stored in the cloud.
Cloud data management is not just for businesses that are reliant on cloud storage. Many companies use a mix of cloud and local data storage. Cloud data management helps them manage all this data in an organized way and, in some cases, even integrates with their data warehouse systems.
With cloud data management, you can optimize your products and services more efficiently and cut down on both operational and capital costs.
How Does Cloud Data Management Differ From Traditional Data Management?
Traditional data management, often called on-premises data management, revolves around managing your organization’s data within the confines of your local network. It extensively handles, stores, and maintains files, databases, and archives that are kept within your company’s hardware systems. IT teams often manually oversee backups, updates, and disaster recovery plans.
On the other hand, cloud data management is the contemporary method of managing data stored over the internet on cloud platforms. The major plus point of this approach is that this not only lets you manage the data stored on the cloud but also the data that resides within your on-premises hardware. It's made to work with different cloud services and opens up new exciting opportunities and also some challenges as compared to traditional methods.
Let’s dive into the key differences between them:
Traditional Data Management | Cloud Data Management | |
Nature Of Tools | Traditional data management tools are generally configured to work within a localized network and often struggle with cloud compatibility. | Cloud data management tools are inherently designed for internet-based data architectures and are compatible across various cloud service providers. |
Data Location | Traditional data management focuses on data stored locally within the organization. This makes remote access a challenge that often requires VPNs or other secure channels. | Cloud data management allows data storage anywhere over the internet, providing easier access from multiple locations. |
Data Integration | Data integration in a traditional environment can be difficult and often requires custom solutions. | Modern cloud data management provides built-in data integration capabilities like APIs and pre-built connectors. |
Flexibility & Scalability | Traditional systems are generally rigid and require hardware investments to scale up. | Cloud-based systems offer real-time scalability and flexibility, often on a pay-as-you-go model |
These differences between traditional and cloud data management tools show how important modern cloud-based solutions are for today's businesses. Take, for instance, Estuary Flow – a fully managed solution that stands out where traditional systems often stumble.
Beyond its built-in data integration features, which include over 100 pre-built connectors, Estuary Flow offers a no-code alternative for seamless data management. With real-time scalability, flexibility, and a pay-as-you-go model, Estuary Flow sets a high standard in cloud data management. We'll look into it in more detail later in the article.
11 Proven Benefits of Cloud Data Management
Now, let’s see how adopting cloud data management can significantly improve your company’s performance.
Enhanced Security Measures
Cloud data management platforms keep your data secure. They use top-of-the-line security features that often outperform traditional on-site systems. 94% of companies that switch to the cloud report better security. These platforms also minimize common risks like hardware failures or device damage, giving you peace of mind about the safety of your sensitive data.
Scalability
Cloud services are incredibly flexible and can adapt to your business needs. Whether you’re experiencing a temporary workload increase or planning for long-term growth, you can easily adjust your cloud services. This means you only pay for what you use, which can cause significant cost savings over time.
Regulated Data Access
Better security doesn’t just protect your data; it also means you can control who has access to it. Cloud storage solutions come with robust data governance capabilities. This makes it easier for team members to access the data they need while also creating and promoting a culture of collaboration within the organization.
Hassle-Free Backups & Quick Recovery
With cloud providers, you don’t need manual data backups. These services handle automated backups and disaster recovery on your behalf. This saves your team valuable time and assures you that your data is safe and current.
This feature particularly helps in emergencies like ransomware attacks. Quick data recovery capabilities minimize downtime and potential losses and ensure your data can be restored promptly.
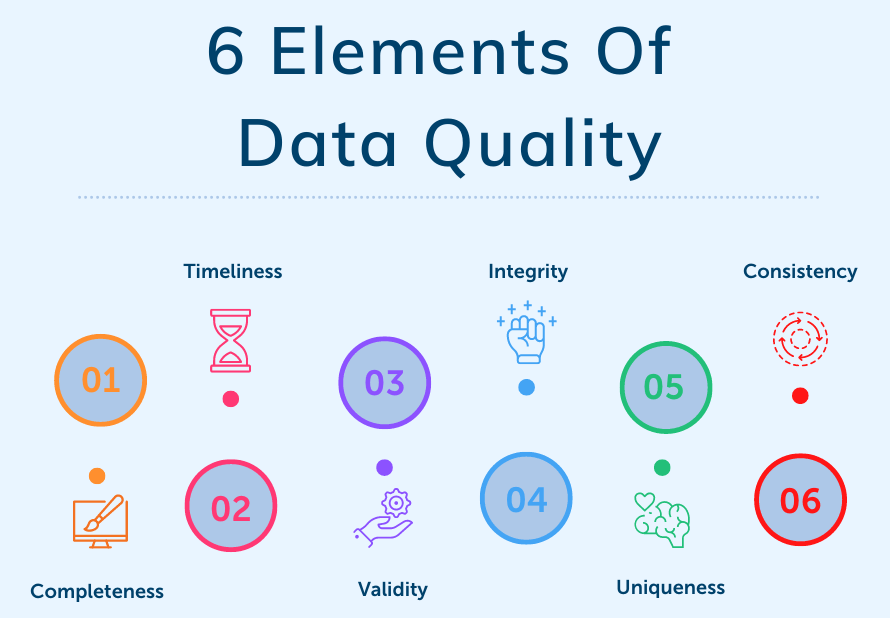
Improved Data Quality
Managing data in the cloud eliminates data silos and integrates all information into one central repository. This centralization improves the data quality, making it clean, consistent, and up-to-date. When you have better data, your organization can perform technical activities like real-time analytics and machine learning applications more effectively.
Seamless Updates
With cloud services, you benefit from hassle-free software updates. Cloud providers handle these automatic application updates which makes the process smooth and straightforward.
This lets your team focus on work tasks. There's no need to halt operations and wait for the IT department to implement system-wide updates. Your overall operational efficiency improves as your applications stay current without disrupting daily activities.
Organized Data Pipeline
Cloud data management strategy focuses on transforming data into actionable insights. It involves many steps like data integration, analytics, and metadata management. These processes let you make informed decisions which in turn result in effective enterprise data management.
Better Big Data Management
Cloud data management can easily handle large volumes of information because it can adjust its resources when needed. So if you’re looking to tap into big data to find new business opportunities and better understand your customers, cloud data management is the way to go.
Unified Enterprise Solutions
Using cloud data management can fix the issue of disjointed systems within an organization. Whether it’s customer data management, product data management, or other specialized needs, these platforms offer a point of integration to streamline overall data management systems.
Easy Mobile Access
With the increasing use of mobile devices in the workplace, easy access to data on-the-go is more important than ever. Cloud data management solutions let you access data from anywhere which improves overall productivity and user experience.
This means employees can work from different locations – be it from home, a café, or even while traveling – and still stay connected to important work data. This accessibility gives you and your business a major advantage.
High Availability & Reliability
Availability and reliability are vital for any business. Cloud providers usually guarantee these through service-level agreements (SLAs). These SLAs are important for business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
These agreements make sure the cloud service will be up and running almost all the time. This reduces downtime risk and gives you peace of mind, knowing you can access data and services whenever you want.
What Are the Risks Associated With Cloud Data Management?
Even though cloud data management brings great benefits like flexibility, easy access, and efficiency, it also comes with some problems. These problems can mess up the advantages you want from migrating to the cloud. To create a strong cloud data management strategy, you should know both the good and the bad sides.
Since we’ve already talked about the benefits, here are the biggest problems that businesses should know about:
Data Breaches & Attacks
One of the major concerns of cloud data management is data security. Cases of data breaches, DDOS attacks, and account hijacking are quite common these days. A cloud data management platform can be vulnerable if they’re not properly secured.
The biggest reason behind this is the sharing of cloud resources among multiple users which opens up security gaps. You need to employ skilled staff to manage these risks, especially when dealing with sensitive data.
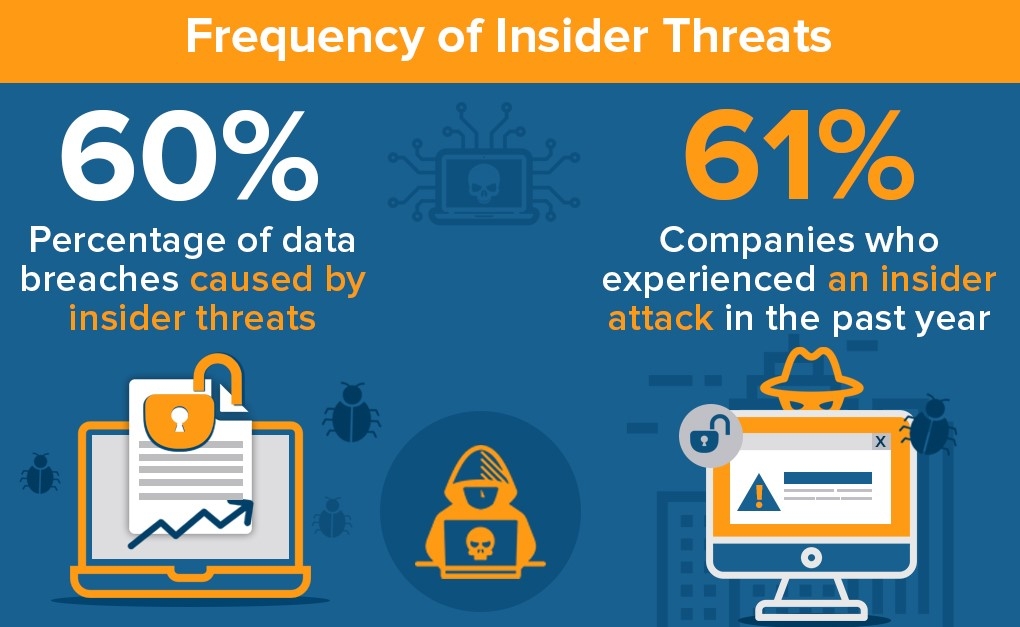
Insider Threats
Both organizations and cloud providers have staff and administrators with authorized access to systems and data. These “insiders” pose a serious risk and almost 60% of data breaches are the result of these insider threats. They can misuse their access rights, intentionally or unintentionally, to compromise data security.
Third-Party Data Hosting
When you store your data on a cloud, a third-party cloud provider hosts that data. For some businesses, this can be a concern, especially if they’re storing sensitive or critical information. Even if the cloud providers take measures for data protection, the data is not in your hands which might not be acceptable in some enterprise data management strategies for sensitive data.
Cost Implications
Cloud storage might seem like a cost-effective solution but that's not always the case. A recent survey revealed that 1/3 of businesses are exceeding their cloud budgets by as much as 40%. Managing the costs of cloud software licenses and resources is also a big challenge. So the financial aspect can be a risk if not properly managed.
Reduced Visibility & Control
Another risk specific to cloud environments is reduced visibility and control over assets and operations. This is a major concern when using external cloud services since some of the policies and infrastructure are the responsibility of the cloud providers. This change makes it challenging to monitor security and data integrity in a cloud environment.
Unauthorized Use & Shadow IT
Cloud platforms make it easy to provision new services – sometimes way too easy. This ease can cause what is known as “shadow IT” where services are set up without proper authorization. Unauthorized services increase the risk of malware attacks and data leakage because they aren't adequately secured. Users should protect their devices with dedicated antivirus software and even consider basic cleanup tools to keep digital clutter to a minimum.
Risks In Management APIs
Cloud providers offer management APIs you use to control your resources. These APIs can be vulnerable to attacks as they’re accessible over the Internet. If these APIs get compromised, it poses major risks to your cloud resources and data.
Multi-Tenancy Risks
Cloud services often use multi-tenancy where multiple users share the same resources. While this is efficient, it increases the risk of one user affecting the others because of system vulnerabilities. The failure to maintain separation between tenants could cause unauthorized data access.
Insufficient Due Diligence
Lack of due diligence increases cybersecurity risks. Businesses sometimes move data to the cloud without fully understanding the implications, their responsibilities, and the security measures in place by cloud providers. This lack of understanding can compromise the overall cloud data management strategy.
Fortunately, there are solutions and best practices that you can leverage to mitigate these risks. Integrating modern, cutting-edge data management platforms in your strategy can help you avoid common pitfalls.
Estuary Flow: Bridging the Gap in Modern Cloud Data Management
When it comes to cloud data management, Estuary Flow stands out as our top-tier ETL tool. If you’re a business looking for quick and reliable data migration and integration, this is your go-to solution. It uses real-time streaming SQL and Typescript transformations to make sure that your data transfers and transforms at a higher speed.
Here are some unique features that make Estuary Flow stand out from the rest:
Cross-Platform Compatibility & Real-Time Data Replication
What sets it apart is how well it integrates with different cloud platforms, databases, and even Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications. It offers real-time data replication so your data remains consistent and up-to-date for both analytical and operational purposes.
Automation for Enhanced Efficiency
Estuary Flow takes care of schema management and data deduplication to simplify your work. This means you can save time as there's no need to bring in extra scheduling or orchestration tools.
Advanced Scalability Features
Flow can handle data changes at up to 7GB/s. This is a powerful feature, especially if you are dealing with databases of different sizes. It keeps data flowing smoothly without compromising performance.
Comprehensive Data Governance
When it comes to data governance, Flow provides absolute authority over your data pipelines. You get complete control over your data pipelines. With built-in schema controls, the tool helps maintain data integrity and accuracy which is vital for any data management strategy, especially management in the cloud.
Integration Capabilities
It comes equipped with more than 100 pre-built connectors, making it easy to integrate data from various sources and endpoints. If a specific connector is not available, you can request it. This flexibility makes Estuary Flow a must-have part of any cloud data management strategy.
Legacy System Compatibility
Still clinging to older systems? Estuary Flow bridges the gap between your traditional legacy systems and modern hybrid cloud environments. This is a big plus if you’re looking for a smooth transition to modern cloud data management without losing your past data or causing data silos.
Customer Data Analytics
Flow isn’t just about moving and managing data; it’s about understanding it, too. The tool gives you a full, real-time view of your customers, enriched by historical data. This feature benefits customer interactions and makes them more personalized and effective.
Distributed System Architecture for High-Volume Data Processing
Estuary Flow is built as a distributed system. It can scale with your data volume and is designed to manage high-volume data processing while maintaining top-notch performance. When it comes to backup data and disaster recovery, Flow effectively meets your enterprise data management needs.
The Takeaway
With proper cloud data management, you can grow at your own pace without being limited by your IT infrastructure. Whether you're a startup with modest data needs or an enterprise with vast sets of information, the cloud can accommodate your requirements and ensure you're never held back by technical constraints.
However, the shift from traditional on-premises data management has certain challenges that must be addressed. Estuary Flow stands out as an advanced cloud data management solution that helps you overcome these hurdles.
With its real-time data replication, automation features, scalability, and integration capabilities, Estuary Flow streamlines cloud data management workflows. Its compatibility across platforms, legacy systems, and databases makes it a versatile tool to meet diverse business needs.
Sign up today for free and experience the benefits firsthand, or connect with our team for further assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cloud Data Management
We'll now tackle some of the most common questions people have about cloud data management, making it crystal clear and easy to understand.
What are the types of clouds?
There are 3 main types of clouds:
- Public Cloud: It is a shared storage space or server farm offered by companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Your data is stored and processed on their servers. It's cost-effective and scalable which makes it suitable for various applications.
- Private Cloud: These are dedicated to a single organization. They can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer more control and security over data which makes them popular in industries with strict compliance requirements, like healthcare or finance.
- Hybrid Cloud: This cloud strategy combines elements of both public and private clouds. You can store sensitive data in your private cloud while using the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds for other tasks. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility and can optimize cost-efficiency based on workload demands.
What are the various cloud models?
Different cloud service models offer various levels of abstraction and management for both data and applications. These cloud service models include:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It includes services like virtual machines, storage, and networking. You can provision and manage your infrastructure components which gives you more control and flexibility while still relying on the cloud provider's hardware.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): PaaS offers a platform that includes infrastructure components but also includes development tools, databases, and application services. It simplifies the process of building, deploying, and managing applications.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. You access these applications through web browsers, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. Popular examples of SaaS include email services, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and collaboration software.
- BaaS (Backup as a Service): BaaS is a cloud service model focused on data backup and recovery. It lets you securely back up your data to the cloud which reduces the need for on-premises backup infrastructure. BaaS providers handle data protection, storage, and restoration.
- AIaaS (Artificial Intelligence as a Service): AIaaS provides cloud-based access to artificial intelligence and machine learning services. You can use pre-built AI models and tools for tasks like natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics without having to build and train your own models.
- DaaS (Data as a Service): DaaS delivers data on-demand over the internet. It provides access to curated datasets, databases, or data analytics tools. DaaS can be particularly useful if you’re looking to access external data sources or monetize your data assets.
How does cloud data work?
Here's how cloud data works:
- Data Storage: It all begins with uploading data to a cloud provider's servers. Cloud providers typically store data redundantly across multiple data centers to ensure data durability and availability.
- Data Access: Authorized users and applications can now access it from anywhere. Access can be controlled through identity and access management (IAM) tools.
- Data Transfer: Data is transferred between the user's devices or on-premises systems and the cloud provider's servers over the Internet.
- Data Processing: A cloud management system offers different services like running virtual machines for custom applications, using pre-built services for specific tasks, or accessing software applications for processing and analyzing data.
- Data Redundancy and Backup: Cloud providers typically replicate data across multiple geographic regions and employ backup mechanisms to protect against data loss because of hardware failures or disasters.
- Data Management Services: Cloud providers offer various data management services, like database management, data warehousing, data lakes, and data integration tools.
How do vendors charge for cloud services?
Pricing for cloud services can vary based on your needs and usage. Some providers offer a subscription model while others use a "Pay as You Go" system. This lets you keep costs low while meeting your specific needs.
Why is cloud data important?
Here are e key reasons why cloud data is important:
- Collaboration: Real-time collaboration increases productivity.
- Data Analytics: Cloud supports advanced analytics and insights.
- Data Security: Cloud providers invest in security measures to protect data.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud storage helps in data recovery during emergencies.
- Cost Efficiency: The pay-as-you-go model reduces capital expenditure on hardware.
- Data Redundancy: Advanced backup strategies ensure data integrity and availability.
- Global Reach: Serve global users with low-latency access via distributed data centers.
- Accessibility: Cloud data is accessible from anywhere which promotes remote work and collaboration.
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources to accommodate changing data needs without upfront hardware costs.

About the author
With over 15 years in data engineering, a seasoned expert in driving growth for early-stage data companies, focusing on strategies that attract customers and users. Extensive writing provides insights to help companies scale efficiently and effectively in an evolving data landscape.
Popular Articles